You are here
Plans
Active forum topics
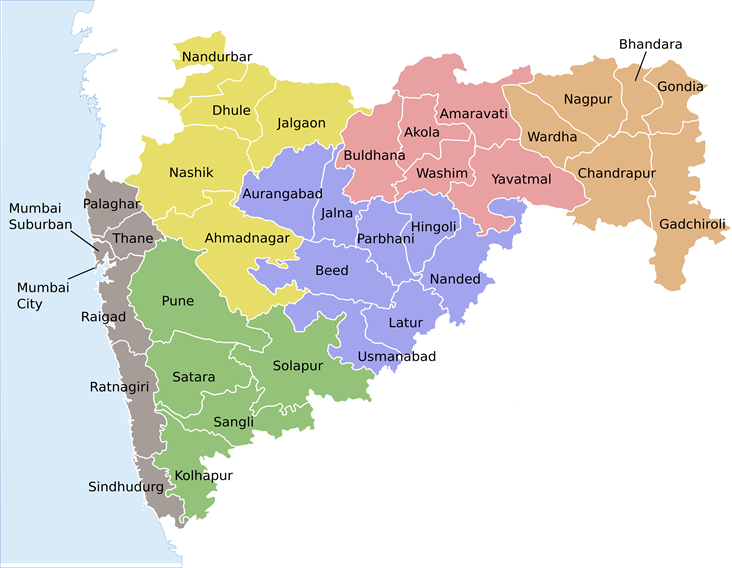
To see the Plan, click on the relevent district
Regional Plans
For the comprehensive development of the districts of the state, for maintaining equilibrium in the development of rural and urban areas, to curb and plan unauthorized and uncontrolled growth in municipal / municipal council areas, Regional plans are prepared showing the proposed land use and public facilities for the development of the rural areas. Regional plans are prepared as per the provisions of section 3 to 20 of the Maharashtra Regional and Town Planning Act, 1966.
The State Government establishes Regional Planning Boards to prepare Regional Plans. There are 36 districts in Maharashtra. All these districts have sanctioned regional plans in force. Separate Regional plans have been prepared for the safe-guarding of environmentally sensitive areas.(Mahabaleshwar-Pachgani Region,Dahanu Region)
Contents of Regional Plan
- Allocation of land for different uses
- Reservation of areas for open spaces, gardens, zoological gardens, animal sanctuaries, dairies etc..
- Water supply, drainage, sewage system and services like electricity etc
- Location of new towns
- Industrial estates, MIDCs
- Tourism development projects
- Transportation and communication
- Military and defence areas
- Irrigation projects
- Development Control
- Implementation strategies
Development Plan
Under the provisions of section 21 to 31 of the Maharashtra Regional and Town Planning Act, 1966, for the areas covered under the jurisdiction of the local bodies such as the Municipal Corporation / Municipal Council / Nagar Panchayat, the provision is made to prepare a draft development plan showing the proposed land use and public facilities as per future population. The plans are approved by the Urban Development Department of the Government
Presently, in the state of Maharashtra, there are 386 local authorities, including 27 municipalities, 17‘A’ class Municipal councils, 72 ‘B’ class Municipal councils, 144‘C’ class Municipal councils and 126 Nagar Panchayats. Out of these, the development plan of all the local authorities have been approved by the government at least once, except for the 122 new Nagar Panchayats and 16 Nagar Parishads. Apart from this, development plans have been prepared for some Grampanchayat areas, for which the Zilla Parishad is the Planning Authority. Due to the requirement of expertise in preparing development plan for the municipal corporation areas, special units have been created headed by Deputy Director, town planning.Some special planning authorities have also been established under the provision of section 40(1b), Area Development Authority under section 42 of the MR & TP Act, 1966. Such Planning Authorities too can prepare the development plan or planning proposals for their areas and implement it after getting the same sanctioned from the Govt.
Contents of Development Plan
- Proposals of zoning for various purposes
- Designation of land for public purposes
- Transport and Communication
- Water supply, drainage etc.
- Sites for community facilities
- Sites for industries
- Preservation, conservation proposals of natural sceneries
- Preservation of features of historical, natural, architectural, heritage interest
- Proposals for flood control etc.
- Development Control & Promotion Regulations
Town Planning Scheme
For the implementation of Development Plans, for the areas covered under the jurisdiction of the Planning Authorities such as Municipal Corporations / Municipal Councils / Nagar Panchayats, or in respect of any land which is likely to be in the course of development or which is already built upon, Town Planning Schemes are prepared with the methods such as micro-level planning and Land Pooling and Reconstitution, under the provisions of section 59 to 112 of the Maharashtra Regional and Town Planning Act, 1966. The Town planning schemes are being sanctioned by the Urban Development Department of the Government.
Implementation of the development plan proposal is the main purpose of town planning schemes. Some of the original Town planning schemes have been prepared by this department and work of some town planning schemes are in progress. The municipal council can charge the betterment charge on the plots which benefit from the Town Planning Scheme, and thus, the costs of the schemes can be recovered. Town planning scheme has proven to be an effective tool for the implementation of the development plan. The main reason for the non-implementation of town planning schemes is the long-duration time required for the preparation of the same. For this, the Directorate has proposed changes in the planning provisions of the Act, and the said changes have also been approved in the legislative assembly.
Principles of Town Planning Schemes
- For implementation of D. P. proposals
- Lands pooled and reconstituted according to some equitable formula.
- Loss of land because of reservation.
- Dispossession kept at bare minimum
- Reconstituted plots : buildable
- Increments, incremental contribution – maximum 50%
- Cost of Scheme : minimum as far as possible
- Urban land should itself resource the cost of development
- Town planning scheme has been provided with an in-built mechanism for arbitration.
- Conceptually, town planning scheme is a joint land development project undertaken by the owners.
- Planning authority steps in as an agent on behalf of owners.
- Provides for smooth vesting of lands to planning authorities for public purposes
- General opposition to acquisition from owners is not existent, therefore, rightly called as ‘land acquisition without tears.’